We are all surrounded by energy work and power formulas. Our bodies in which we live are energy conversion machines. Not only our bodies but all living creatures across the globe are energy conversion machines.
You might wonder how are our bodies energy conversion machines. There is a chemical process going on every day and energy minute in our bodies.
The energy within our system, also known as chemical energy, stores energy, which is our food that converts the stored food into work, energy, and power that we utilise to process our day-to-day functioning. This chemical energy is stored in fatty tissues. It all depends on how we eat and the level of physical activities of our body.
On the other hand, if we consume more food than our body consumed by our body to work and function, the left out energy is stored as body fat. This body fat is a serious problem nowadays as we eat more than what is required due to our sedentary lifestyle.
Before we deep dive further into various aspects of each of these concepts, let us understand Work, Energy and Power meaning.
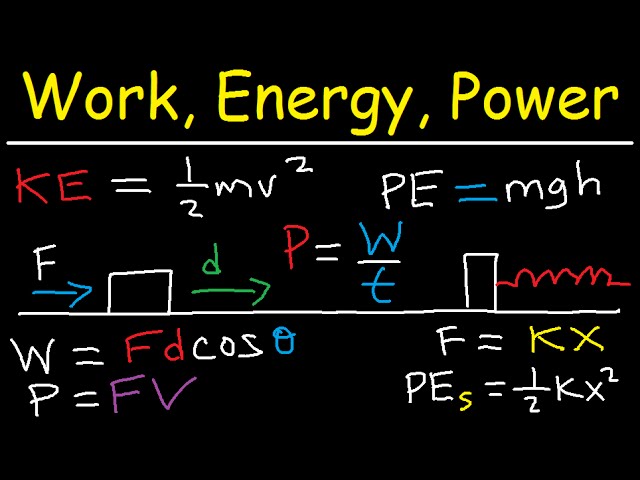
Work
Work is defined as the transfer of energy. As per the definition by science, work is applied to an object when you apply force or transfer energy to that object. This means that when one object tends to transfer the energy to another object, the first object is working on the second object. This is called work.
Examples of work are pulling and lifting. If you pull any object, the energy is transferred from you and focused on pulling the object. This activity is known as work.
Principle of Work: The change in the kinetic energy of an object is equal to the net work done on the object.
Energy
We have already explained a part of the energy at the beginning of this article. We will now try to understand the aspects of energy in a more detailed manner.
It is defined as the capacity of performing tasks and do any work. An excellent example of energy is that when we are trying to pull or push something. The force that we apply in doing such activities is considered energy. The amount of energy of any moving object is known as Kinetic energy.
Types of Energy
There are two types of energy
- Kinetic Energy – It is the energy of motion
- Potential Energy – It is stored energy
Forms of Energy
The various forms of energy include Atomic energy, solar energy, electrical energy, chemical energy, mechanical and heat energy.
Solar Energy – This is a natural energy that is provided by the rays of the sun. It is utilised as Radio Waves, Gamma Rays, Microwaves & Ultraviolet light. These are some examples of solar energy.
Electrical Energy – The use of electric power over duration is stated in kilowatt-hour, megawatt & gigawatt.
Nuclear or Atomic Energy – Nuclear reactions release this one. When a neutron splits into smaller pieces, it is called fission.
Understanding Energy as per the human body
Energy consumed when we rest
The amount of energy utilised by the body to sustain energy to live and perform various activities is known as metabolic rate. Energy consumed by humans is converted to work, thermal energy, and stored fat.
By far, the largest fraction goes to thermal energy, although the fraction varies depending on the type of physical activity. When a person rests, the total energy consumed by the body is considered as basal metabolic rate (BMR).
When stored through the consumption of food, this energy is stored in the body to perform future activities. This is where food is utilised within the body to perform various functions such as thinking, running, breathing, and various internal and external performance.
The human body is thus considered the perfect example of work, energy, and power.
Also, Read: Essential Aspects of Bitcoin Mining
Power
In the human body, power is consumed when you work, such as physical activities that include lifting weights etc. Mostly it is considered as the work which is done outside the world. Skipping, running, climbing stairs and some such examples of applying power.
In scientific words, power is the work done in a unit of time. It is a measure of how quickly work can be done. The unit of power is the Watt = 1 Joule/ 1 second.
One common unit of energy is the kilowatt-hour (kWh). If we are using one kW of power, a kWh of energy will last one hour.
Calculating Work, Energy and Power
Because energy is the capacity to do work, we measure energy and work in the same units (N m or joules). Power is the rate of energy generation over time. Power’s standard unit of measurement is the Watt.
Watt represents the generation or absorption of energy at the rate of one joule/sec. Power’s unit of measure in the English system is horsepower, which is equivalent to 735.7 Watts.
Examples of Work, Power & Energy
The human body converts energy stored in food. It is utilised in work, thermal energy or chemical energy that is stored in fatty tissue. The rate at which the body uses food energy to sustain life and to do different activities is called the metabolic rate.
Also, the rate when the body is at rest is known as the basal metabolic rate. This js when the body performs internal functions and energy is utilised. The complete consumption of energy is with the liver and spleen. The utmost utilisation is with the largest part of the body, which is the brain.
The consumption of energy during the performance of various activities can be determined by measuring the oxygen level of people. This is because of the process of is oxidising food.
Conclusion
In this article, we have understood the work, power & energy basis human body. Work is considered a transfer of energy. Energy is the amount of action performed through physical work & power is the amount of energy utilised.